The Issue
Our Application (Diagnosoft Virtue) needed to have a scalable servers farm so that when the load increases on the existing servers, an auto scaling mechanism should expand the servers farm by adding another servers to it, and a load balancing technique should balance the load between the launched servers, so that the new client can be served smoothly with high performance and without affecting any of the existing clients.
To achieve this we assumed that each server (Amazon m3.large) can serve up to 3 clients if they used our application to the maximum resource consumption, so we measured the server load by the number of virtue clients not by the common readymade measures like memory or CPU efficiency, which is not exists in the exciting metrics, so we developed a custom metrics called Userslimit using .Net and AWS SDK to calculate the number of clients per server and send an alarm every 5 mins to the auto scaling, the developed application which sends this measure should be running on the back-end server to read from the database the connected number of clients.
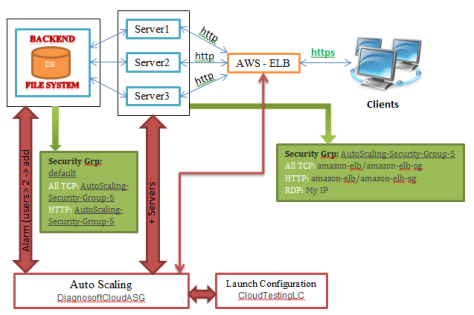
The issue is that ELB (elastic load balancer) of AWS is not balancing the load evenly among the available servers although it’s mentioned that it uses round robin algorithm in balancing, its detailed mechanism is not clearly determined in AWS help docs but the articles on the internet assumed that ELB uses range of IPs automatically assigned for each available server behind the ELB, so when a request comes from a client it checks its IP falls in which range of IPs and assigned it to the relevant server. So we can find many clients fall within the same range of IPs assigned to a server while other servers are not utilized, which might lead to bad performance for connected clients, the figure above describes the old mechanism for load balancing and auto scaling.
The Proposed Solution
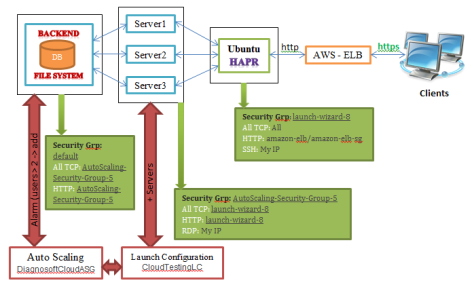
After researching and reading multiple articles we came up to use HAProxy instead of ELB, HAProxy is a free open source load balancer, available to be installed on UNIX machine, the figure above describes the new architecture of the load balancing and auto scaling mechanism.
HAProxy provides low level configuration and adjustments so that it can be configured according to our needs and to whatever balancing algorithm that best fit our needs, we chose least connection algorithm for balancing as it is best for longer client sessions in which the new client requests are directed to the server with least connections to it.
How we achieved that
- Launch new EC2 instance with Ubuntu operating system and named it Ubuntu HAProxy
- Connect to the Ubuntu instance from windows using PuTTY (PuTTY is a free (MIT-licensed) Win32 Telnet and SSH client)
PuTTY Download page: http://www.chiark.greenend.org.uk/~sgtatham/putty/download.html
Instructions: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSEC2/latest/UserGuide/putty.html?console_help=true
- Install HAProxy and configure it simply by modifying a configuration file called haproxy.cfg ,
Refer to the below link to Install HAProxy on Ubuntu and to know some basic configurations:
https://serversforhackers.com/load-balancing-with-haproxy
- After installing HAProxy you can run the command sudo nano /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg in PuTTY to modify the file.
Sudo: super user do (gives you privilege of modifying the file)
Nano: is a text editor
/etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg: the path of the HAProxy configuration file
- In order to achieve auto scaling, install a component on Ubuntu from GitHub called haproxy-autoscale which updates the configuration file haproxy.cfg every minute with the current available servers, the component uses a template for haproxy.cfg that can be modified as needed to match the configuration we want, to install it do the following:
- Download the installation from: https://github.com/markcaudill/haproxy-autoscale#description
- Extract the files and copy it to the Ubuntu machine in this location /home/ubuntu/ using a file transfer software called WinSCP that can be installed on windows machine from: https://winscp.net/eng/download.php
- Run the command sudo python /home/ubuntu/setup.py install from PuTTY
- You can modify the template from this location /home/ubuntu /templates/haproxy.tpl
(below is the configuration template we used including stickiness and checks)
- To make the auto scale run every minute, create a job on the Ubuntu machine that runs a specific file in haproxy-autoscale which is responsible to update the configuration file haproxy.cfg with the specific given parameters,
To create new job:
- Run this command in PuTTY to open a text file where you register a job: export VISUAL=nano; crontab -e
- Write the below command at the end of the file:
* * * * * /usr/bin/python /home/ubuntu/update-haproxy.py –access-key=’your-access-key’ –secret-key=’your-secret-ke’ –security-group=’security-group-of-the-servers’ –output=’/etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg’
- Removed the load balancers from the auto scaling in AWS to prevent attaching the scaled instances to ELB.
- After doing all this and running the Ubuntu machine steadily, attach it to ELB manually from the edit instances button, and if it’s there but out of service we run the command sudo service haproxy reload in PuTTY to reload the HAProxy and remove it from ELB then re-add it again.
- Log in to http://{IP of the Ubuntu machine}:10005/haproxy?stats to monitor the HAProxy load balancer and the servers activity.
Hope this article helps anyone has similar issues, don’t hesitate to ask me anything related 🙂